A group of U.S. senators last week proposed yet another bill to revive the domestic chip industry, theAmerican Foundries Act of 2020 (AFA).
This new bipartisan proposal is the second such measure in a month, following the Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors (CHIPS) act, introduced on June 10.
The two initiatives highlight the effort by the U.S. government to localize the electronics supply chain and rebuild the domestic semiconductor industry now that most of the world’s production has shifted to Asia.
The AFA would provide grants to U.S. states to help expand commercial chipmaking facilities while CHIPS would mainly fund projects run by the Pentagon and other government agencies. Funding for the AFA would be approximately $25 billion while CHIPS comes in at about $12 billion.
The proposed bills also follow a separate effort by the administration of U.S. President Donald Trump to attract investment by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) in a new $12 billion chip facility with industry-leading 5nm technology in the state of Arizona.
TSMC has said its project in Arizona would draw additional investment from other companies that are part of its production ecosystem.
While the chip industry started in U.S., the nation is at risk of falling behind in production as countries in Asia, especially China, have made significant investments in chipmaking, Senator Jim Risch (R-Idaho) said in a June 26 press statement. Seventy-eight percent of the world’s advanced chipmaking capacity is located in Asia, the statement said. North America fell behind China for the first time in 2019, according to the statement.
“With the Chinese Communist Party’s continued efforts to dominate the rest of the world’s microelectronics industries through theft and coercion, it is critical that we work swiftly to strengthen domestic production of semiconductors and maintain our strategic competitive edge,” said Senator Risch.
The AFA would prohibit any firms owned, controlled or otherwise influenced by the Chinese government from accessing funds provided by the legislation.
Other sponsors of the AFA are Tom Cotton (R-Arkansas), Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.), Josh Hawley (R-Missouri), Jack Reed (D-Rhode Island), Kirsten Gillibrand (D-N.Y.), Susan Collins (R-Maine), Angus King (I-Maine) and Doug Jones (D-Alabama).
“Our nation is in an economic crisis,” Gillibrand said in the press statement. “Investing in microelectronics manufacturing and the semiconductor industry will create high-paying manufacturing jobs for hard-working Americans at a time when our country needs it most. Additionally, this bill helps to strengthen our microelectronic domestic supply chain, prioritize American-owned businesses over foreign production, and keep our country safe.”
AFA funding
The AFA would authorize the U.S. Department of Commerce to award $15 billion in grants to states to assist in the construction, expansion, or modernization of semiconductor fabs, as well as assembly, test, advanced packaging, or advanced research and development facilities.
The AFA would also authorize the U.S. Department of Defense to award $5 billion in grants for the creation, expansion, or modernization of one or more commercial fabs or advanced R&D facilities capable of producing secure and specialized chips for defense and intelligence purposes. This funding would likely go to commercial facilities capable of producing secure microelectronics, the statement said.
The AFA would also authorize $5 billion in R&D spending to secure U.S. leadership in microelectronics. It would also require government agencies that receive this funding to develop policies to require domestic production, to the greatest extent possible, for any intellectual property resulting from R&D pursuant to these funds. DARPA (the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) would receive $2 billion of the funding.
CHIPS funding
CHIPS for America would earmark at least $12 billion to fund existing Pentagon electronics “resurgence” efforts while spreading $5 billion across other federal agencies for semiconductor R&D. The largest chunk — $5 billion — would fund an IC packaging and assembly institute. That effort also would also create a $500 million investment fund to support a domestic advanced microelectronics packaging ecosystem.
The swirl of activity around chip manufacturing and tightening technology supply chains comes amidst a U.S.-China standoff over semiconductor technology. The campaign includes the use of American export controls to block Chinese access to U.S. advanced IC manufacturing gear. The primary target is telecommunications giant and 5G leader Huawei.
TSMC’s Arizona plan
Prior to the announcement of the AFA and CHIPS proposals, the Trump administration appeared confident that an agreement with TSMC to build a fab in Arizona was imminent.
“TSMC’s plan to build a $12 billion semiconductor facility in Arizona is yet another indication that President Trump’s policy agenda has led to a renaissance in American manufacturing and made the United States the most attractive place in the world to invest,” Commerce Department Secretary Wilbur Ross said in a May 14 statement. “This plan is the result of years of close collaboration among TSMC, the governor of Arizona and his staff, and the administration.”
TSMC still has some reservations. In order for the deal to be finalized, the U.S. federal and state governments would need to provide subsidies to bring TSMC’s production costs in Arizona on a par with its facilities in Taiwan, according to TSMC Chairman Mark Liu.
TSMC has the world’s most advanced 5nm production technology with foundry customers that range from Apple to Xilinx. Samsung of South Korea is in a close race with TSMC to dominate the foundry business and world-leading technology. Their closest competitor is Intel, which has stumbled with its introduction of 10nm technology.
The AFA and CHIPS initiatives would favor chipmakers with headquarters in the U.S. such as Intel, Micron and GlobalFoundries.
Taiwan-based TSMC has one fab in the U.S., WaferTech, in Camas, Washington. The facility was founded in June 1996 as the first dedicated foundry in the United States.
The post U.S. Chip Proposals Seek to Revive Domestic Manufacturing appeared first on EE Times Asia.
from EE Times Asia https://ift.tt/3g6WPlw









 There is a growing use of cloud communication due to the ease of remote working, besides high efficiency and reduced complexity through the integration of real-time capabilities in communication. Chaitanya Chokkareddy, chief innovation officer, Ozonetel discusses how cloud communication and artificial intelligence (AI) can revolutionise the traditional approach in businesses, in an exclusive interaction with […]
There is a growing use of cloud communication due to the ease of remote working, besides high efficiency and reduced complexity through the integration of real-time capabilities in communication. Chaitanya Chokkareddy, chief innovation officer, Ozonetel discusses how cloud communication and artificial intelligence (AI) can revolutionise the traditional approach in businesses, in an exclusive interaction with […]



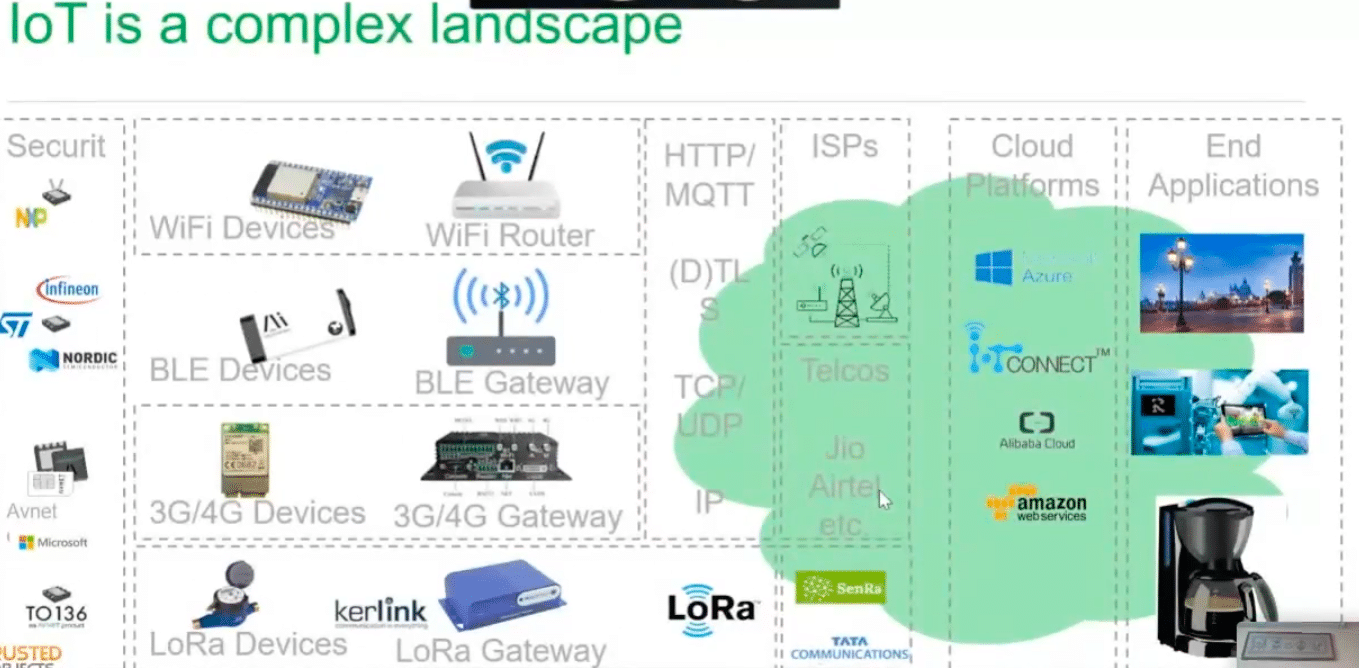 The IoT explosion has put the spotlight on cybersecurity as governments and businesses strive to keep their software and systems safe amidst an increase in cyberattacks. IoT security, on the other hand, has often been overlooked. In fact, most IoT devices lack the basic security features of even a standard home computer system. In this […]
The IoT explosion has put the spotlight on cybersecurity as governments and businesses strive to keep their software and systems safe amidst an increase in cyberattacks. IoT security, on the other hand, has often been overlooked. In fact, most IoT devices lack the basic security features of even a standard home computer system. In this […]

















 e-Mobility and electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure are some of the key focus areas, and relentless research is being done to address high performance in all functional blocks. With the push to move to electric mobility at a national scale, and with the government being very enthusiastic about deployment of electric vehicles (EVs), the electronics […]
e-Mobility and electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure are some of the key focus areas, and relentless research is being done to address high performance in all functional blocks. With the push to move to electric mobility at a national scale, and with the government being very enthusiastic about deployment of electric vehicles (EVs), the electronics […] OnRobot’s robotic tools facilitates flawless collaboration with industrial robots Two of its revolutionary products, OnRobot Screwdriver and the Gecko Single Pad gripper allow ease in flow of processes Denmark-based OnRobot, a provider of robotic tools for collaborative applications is introducing its One System Solution in India. This system enables seamless integration of OnRobot’s products with […]
OnRobot’s robotic tools facilitates flawless collaboration with industrial robots Two of its revolutionary products, OnRobot Screwdriver and the Gecko Single Pad gripper allow ease in flow of processes Denmark-based OnRobot, a provider of robotic tools for collaborative applications is introducing its One System Solution in India. This system enables seamless integration of OnRobot’s products with […] ) and gallium nitride (CoolGaN) technologies, Infineon continues to set standards. The online trade show will open its doors with all product information available on 1 July. The highlight products are:
) and gallium nitride (CoolGaN) technologies, Infineon continues to set standards. The online trade show will open its doors with all product information available on 1 July. The highlight products are: Infineon’s new BMS IC maintains longevity of batteries in hybrid and electric cars It also lessens the disruptions caused by interfering signals on the measurement results Battery management systems (BMS) ensure that the capacity of a battery is optimally utilized so that the longest possible range is achieved by an electric car and that the […]
Infineon’s new BMS IC maintains longevity of batteries in hybrid and electric cars It also lessens the disruptions caused by interfering signals on the measurement results Battery management systems (BMS) ensure that the capacity of a battery is optimally utilized so that the longest possible range is achieved by an electric car and that the […] Maxim Integrated’s new Arm Cortex-M4-based MCU provides reliable operation uninterrupted by bit flips Also allows developers to offer a low-power solution Maxim Integrated has launched the MAX32670, a low-power Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller (MCU) with floating-point unit. The device protects all embedded memory for both flash and SRAM with error-code correction (ECC) to provide the highest […]
Maxim Integrated’s new Arm Cortex-M4-based MCU provides reliable operation uninterrupted by bit flips Also allows developers to offer a low-power solution Maxim Integrated has launched the MAX32670, a low-power Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller (MCU) with floating-point unit. The device protects all embedded memory for both flash and SRAM with error-code correction (ECC) to provide the highest […]
 IR HiRel presents new QPL-qualified radiation-hardened MOSFETs for satellite bus power distribution systems and payload power supplies Has the ability to maintain system reliability by offering a direct thermal path for heat transfer Attaching surface mount hermetic power packages to PCBs in an effective manner is a common challenge faced by space system designers. Very often, […]
IR HiRel presents new QPL-qualified radiation-hardened MOSFETs for satellite bus power distribution systems and payload power supplies Has the ability to maintain system reliability by offering a direct thermal path for heat transfer Attaching surface mount hermetic power packages to PCBs in an effective manner is a common challenge faced by space system designers. Very often, […]